APS Talent Segmentation Process
Talent segmentation enables agencies and work areas to consider and prioritise development and career management for individuals. It is a process that allows executives to consider all employees using a common approach and schedule providing insight into individuals and the cohort as a whole.
The talent segmentation toolkit provides HR practitioners and managers with resources to conduct workforce segmentation using the APS Talent Segmentation Model (formerly the APS Nine-Box Grid).
The resources are designed as a common starting point for agencies while allowing for customisation to suit specific requirements.
Background
One of the most common talent segmentation tools is the nine-box grid, which was originally developed by McKinsey for General Electric in the 1970’s to determine which business unit to invest in[1]. The matrix was later adapted by human resource professionals to identify and prioritise development in employees with the highest potential.
In 2015, the Secretaries Board agreed to implement an APS-tailored nine-box grid to create greater consistency when assessing and developing workforces across the APS. SES Band 1 and Band 2 Officers were identified through a nine-box grid process as high performing and high potential could then be nominated for cross-agency talent council programs.
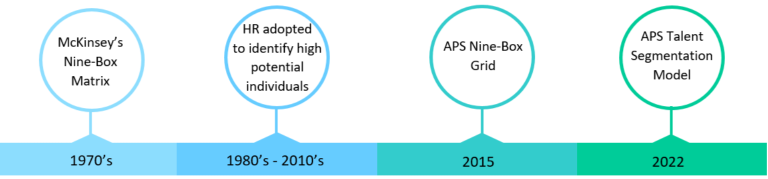
2022 Review & Update
In 2022, the APSC and APS Talent Working Group reviewed the APS Nine-Box Grid (the Grid) and explored a range of alternative talent segmentation models. These consultations reflected that the Grid had been used by many agencies and it was found to be a valuable tool to provide a high level overview of the workforce’s strengths and guide more focused and deliberate development of individuals. The review also found that:
- Agencies that had customised the Grid to their context found it most valuable.
- The Grid had been used by agencies to achieve different purposes (e.g. to identify high potential employees or inform capability development as part of performance processes).
- The Grid would benefit from a number of updates, which included:
- Incorporating a greater development focus to guide next steps.
- Updating to be more developmentally focused, which includes reviewing the titles of the boxes.
- Reflecting specialist leaders as well as generalist leaders.
- Creating a range of additional tools and guidance materials to support managers and HR professionals to implement talent segmentation and development in their agency.
The updated APS Talent Segmentation Model reflects these recommendations and recognises that potential can grow over time and individuals will demonstrate different levels of potential at different times and stages of their career. An individual’s development requirements will also change dependent on this.
To reflect the updated purpose of the APS Nine-Box Grid, it was renamed to the APS Talent Segmentation Model.
How to implement talent segmentation
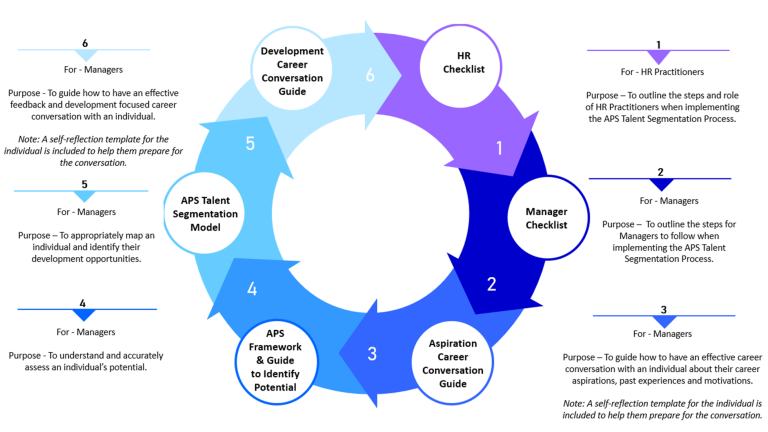
Implementing talent segmentation involves six steps:
- Putting in place the foundations for talent segmentation including determining the objective. For example, minimising succession risk, and communicating about the approach to participants and managers.
- An Aspiration Career Conversation with each participating individual to understand their experience, their aspirations and what motivates them.
- An assessment of potential and performance:
- Understanding of individual’s performance can be gained as a result of assessments and feedback provided through the agency’s performance management systems.
- Understanding of potential can be gained by using the APS Framework and Manager’s Guide to Identifying Potential. More rigorous formal assessment of potential using instruments such as 360 degree assessments can also be undertaken depending on the criticality of the role, the maturity of an agency’s feedback culture and the resources available
- Mapping individuals on the APS Talent Segmentation Model, discussing and moderating the results and identifying development opportunities.
- A Feedback and Development Conversation with each participating individuals to provide input into their development plan (this may include sharing where the individual is currently located in the matrix and why).
- Implementing development actions and continuous review.
Talent segmentation should not be a once off process. Placement and conversations should be revisited regularly, at least annually, to ensure that shifts in an individual’s potential, performance and career goals are reflected.
Resources to implement talent segmentation
The toolkit contains a number of practical guides and templates. It is recommended that the resources are referred to in order to achieve an effective, safe and development focused workforce segmentation process:
- To outline the steps and role of HR Practitioners when implementing the APS Talent Segmentation Process.
- To outline the steps for Managers to follow when implementing the APS Talent Segmentation Process.
- To guide how to have an effective career conversation with an individual about their career aspirations, past experiences and motivations. Note: A self-reflection template for the individual is included to help them prepare for the conversation.
- To understand and accurately assess an individual’s potential.
- The Development Indicator may be used as a visual aid to indicate the strengths and development needs of an individual.
- To appropriately map an individual and identify their development opportunities.
- APS Talent Segmentation Model Descriptors provide further detail to assist managers to accurately identify and map individuals within the Model.
- Printable APS Talent Segmentation Model provides a printable version of the model for managers who wish to map individuals with pen and paper.
- To summarise the individual/cohort-wide results and allow for discussion and moderation of placements on the APS Talent Segmentation Model.
- To guide how to have an effective feedback and development focused career conversation with an individual. Note: A self-reflection template for the individual is included within this Guide to help them prepare for the conversation.
A process map is included below to visually display the order that the resources should be used:
Reference
- Coyne K (2008) ‘Enduring Ideas: The GE–McKinsey nine-box matrix’, McKinsey & Company website, accessed 20 April 2022.



